Here are a few tips on how to prevent infectious diseases, inspired in the guidelines published by the Harvard Medical School, section of Public Health.
The main idea is to avoid getting sick
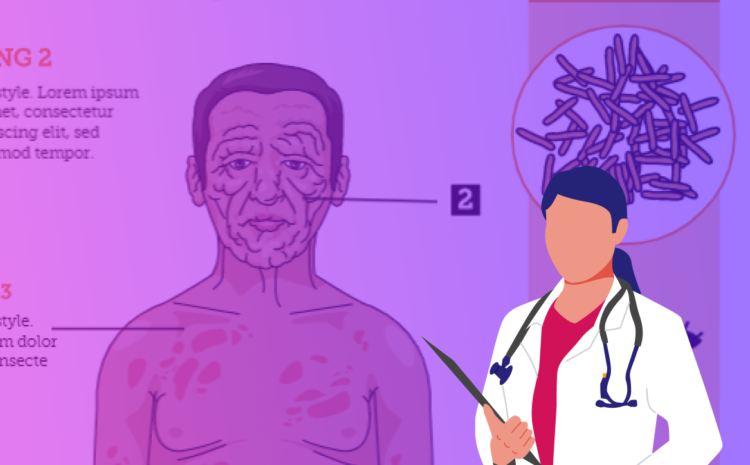
Infections are caused by microscopic organisms known as pathogens—bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites—that enter the body, multiply, and interfere with normal functions. Infectious diseases are a leading cause of illness and death in many places around the world.
Certain people are under particular risk of getting infectious diseases, like those with underlying cardiac illnesses, oncology patients, or those who are taking immunosuppressive medications. For most healthy people, however, following a few basic principles can go a long way in helping to prevent infections.
Understanding how infections diseases are transmitted can help you avoid getting sick
Not long ago, no one understood that infectious diseases were caused by tiny organisms that moved from person to person. Even now, although we know that microscopic living microbes cause disease, how they do so is not always obvious. But we do know that most microbes enter through openings in the body—our noses, mouths, ears, anuses, and genital passages. They can also be transmitted through our skin through insect or animal bites. The best way to prevent infections is to block pathogens from entering the body.
Good hygiene: the primary way to prevent infections
The first line of defense is to keep germs at bay by following good personal hygiene habits. Prevent infection before it begins and avoid spreading it to others with these easy measures.
1) Wash your hands well. You probably wash your hands after using the bathroom, before preparing or eating food, and after gardening or other dirty tasks. You should also wash up after blowing your nose, coughing, or sneezing; feeding or stroking your pet; or visiting or caring for a sick person. Wet your hands thoroughly. Lather up with soap or cleanser, and rub it into the palms and backs of your hands and your wrists. Be sure to clean your fingertips, under your nails and between your fingers. Rinse under running water. Dry your hands and wrists thoroughly.
2) Cover a cough. Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when you sneeze or cough, then dispose of it. If no tissue is handy, cough or sneeze into your elbow rather than into your hands.
3) Wash and bandage all cuts. Any serious cut or animal or human bite should be examined by a doctor. Do not pick at healing wounds or blemishes, or squeeze pimples.
4) Stay at home when you’re sick of infectious disease. That’s the easy one. Just get a Playstation and stay cool, you will recovery naturally from the most common infectious diseases.
5) Avoid touching your eyes, mouth, nose. Avoid making direct contact with napkins, tissues, handkerchiefs, or similar items used by others.
6) Don’t share dishes, glasses, or eating utensils.
Vaccinations are essential if you are to avoid getting sick
Consult your health care provider regarding your immunization status.
In general:
- Children should receive the recommended childhood vaccinations.
- Adults should make sure their vaccinations are up to date.
- When traveling abroad, check with your health care provider about additional immunizations.
- Make sure your pet’s vaccinations are up to date, too. In addition to protecting your pet, this will also protect you and your family.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual
communication in science.