What is DMT?
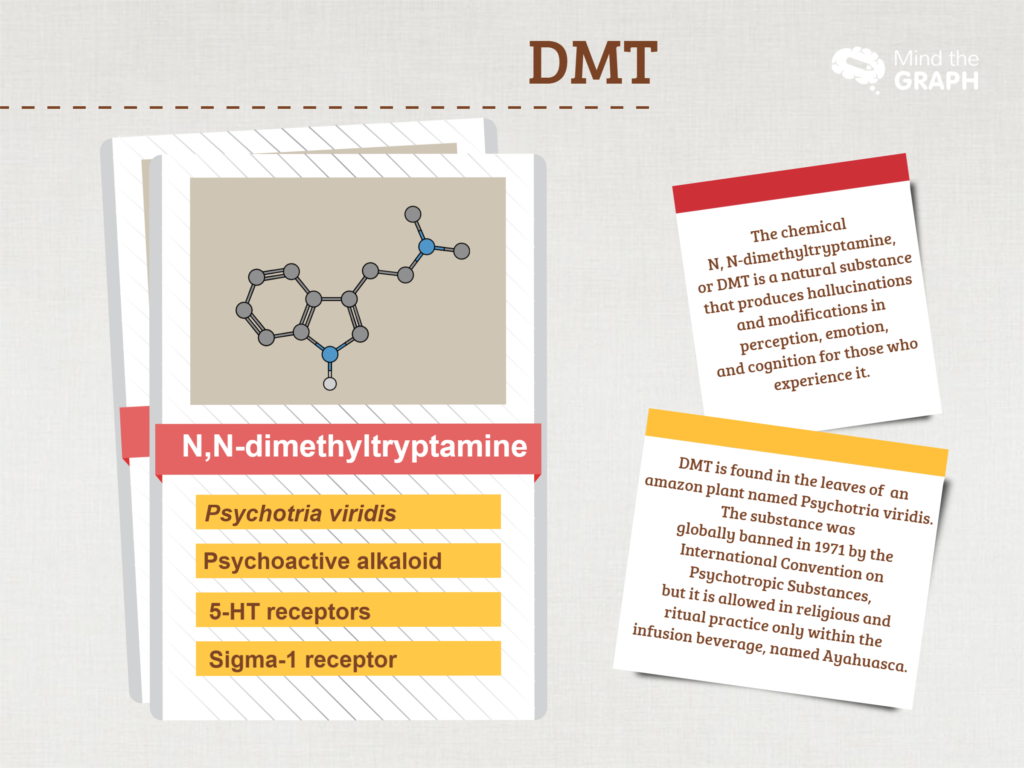
DMT, or N, N-dimethyltryptamine, is a natural substance present in the leaves of an amazon plant named Psychotria Viridis, which is used within the Ayahuasca beverage that produces hallucinations and modifications in perception, emotion, and cognition for those who experience it.
Classified as a psychoactive alkaloid substance, the DMT was globally banned in 1971 by the International Convention on Psychotropic Substances, its consumption is allowed in religious and ritual practice only within the infusion beverage, named Ayahuasca.
Although Ayahuasca is around for more than a century, only in the past few years it has attracted scientist’s attention due to its (yet) non-proven benefits.
The beverage has been presented to improve quality of life and treat patients with neurological and emotional disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and addiction.
What researchers know about the DMT
An article published by the Journal of Affective Disorders Reports analyzed data from the Global Ayahuasca Project’s (GAP) survey involving 11,912 people, who had experienced the infused beverage. In the survey, participants that reported having depression or anxiety before consuming ayahuasca said that after the experience they noticed some level of improvement in their symptoms. Hence, improving their quality of life.
Patients’ reports like this one collected by the GAP, are increasing in the past few years. Despite being good news, scientists and doctors need more complete and detailed physiological studies to understand the source of these Ayahuasca benefits. The infusion-plant beverage has several substances within and each one of them can trigger a different type of response in the human body.
Among these substances, one of them is DMT. This Ayahuasca substance has been attracting researchers’ attention due to its apparent neurogenesis potential.
What is neurogenesis?
Neurogenesis is defined as the process of transformation of neural stem cells or progenitor cells into new neurons. It also involves many different cellular activities, including proliferation, migration, and differentiation of cells.
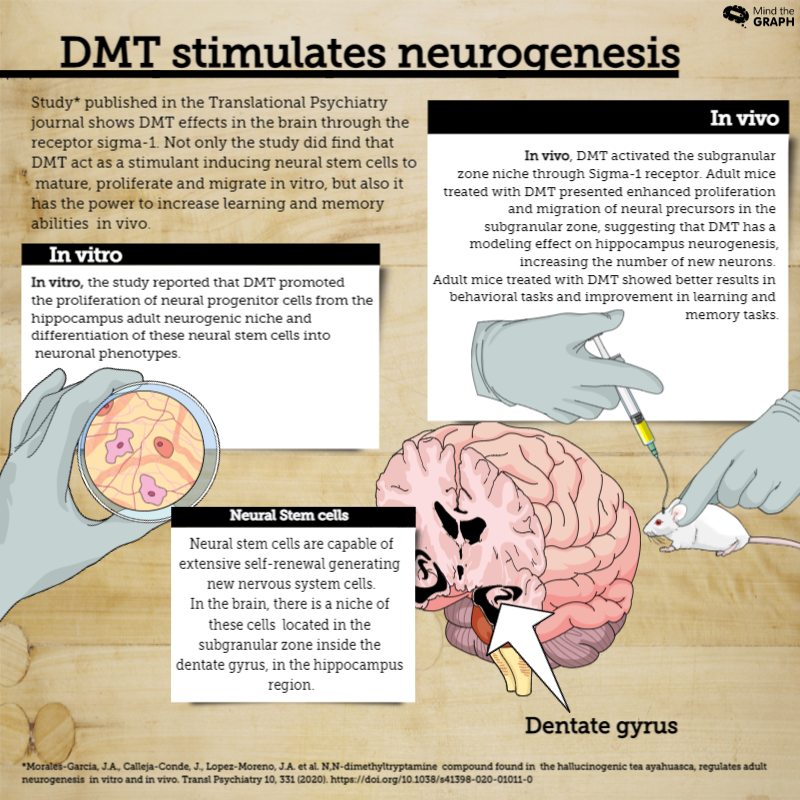
In turn, neural stem cells are capable of extensive self-renewal generating new nervous system cells, for instance, neurons or glial cells. Within our brain, there is a niche of neural stem cells located in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus, in the hippocampus.
The hippocampus is the part of the brain responsible for our memory and learning abilities. This brain region is part of the limbic system and has an important role in turning short-term memory into long-term memories.
In neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, the hippocampus is the first region to suffer, leading to memory decline.
How DMT affects the brain?
For a while, it was thought that DMT only bonded to serotonin receptors 5-HT, which produce its hallucination effects. However, recent studies report that DMT also binds to another receptor type, a non-serotonergic receptor named sigma-1 receptor or S1R.
This receptor is widespread in the central nervous system, especially in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus.
Furthermore, researchers discovered that binding to this receptor S1R, DMT loses its psychoactive effects, not producing hallucinations or modifications in the perception.
Research in vitro and in vivo
A study published in the Translational Psychiatry Journal in 2020, was focused on studying DMT effects in the brain through the sigma-1 receptor.
Using 5-HT antagonists, researchers observed that DMT stimulates neurogenesis through S1R.
In addition, data showed that DMT not only acts as a stimulant inducing neural stem cells to mature, proliferate and migrate in vitro, but also increases learning and memory ability in vivo.
In vitro, the authors of the study reported that DMT promoted the proliferation of neural progenitor cells from the hippocampus adult neurogenic niche. This action increased the number and size of the neurospheres after a week of treatment with DMT.
Furthermore, based on the expression of specific proteins researchers also noticed that DMT promoted the differentiation of these neural stem cells.
Proteins that are found exclusively in young and in mature neurons, called β-III-tubulin and MAP-2, had their expression increased in the neurospheres treated with DMT. This means that DMT promotes differentiation into the neuronal phenotype.
Researchers also noticed the promotion into other cell phenotypes such as astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, all through S1R.
In vivo, DMT seemed to activate the subgranular zone niche through S1R.
Adult mice treated with DMT had “enhanced proliferation and migration of neural precursors in the subgranular zone,” according to the article. This result suggests that DMT has a modeling effect on hippocampus neurogenesis, increasing the number of new neurons.
In practice, adult mice treated with DMT showed better results in behavioral tasks compared to the ones who did not. The treated group presented results of improvement in learning and memory tasks.
The conclusion
All these results are great news for the medical community.
This shows that it is possible not only to stimulate neurogenesis with DMT but also to achieve these results without the hallucinogen effects through a specific receptor.
“This capacity to modulate brain plasticity suggests that it has great therapeutic potential for a wide range of psychiatric and neurological disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases”, said José Ángel Morales in a statement, one of the authors of the article.
These results may strongly influence future studies involving Ayahuasca and DMT. Understanding how to control and how to influence the neurogenesis process could change completely the way neurodegeneration diseases are treated.
Nonetheless, there is a high demand for studies to scientists fully understand the role of substances like DMT, and promising receptors such as sigma-1 receptor, in neurogenesis.
Along with a positive perspective, this could lead not only to new neurodegenerative disease treatments but also to a cure of the diseases.
__________________________
Did you like the infographics made with results presented in the scientific article?
These infographics were made using ready templates available in Mind the Graph, this one and this other one. I made a few changes and in a short time, it was ready!
You can do the same for your research work, you don’t need to start from scratch. Check all the templates available in Mind the Graph.
And start to work on your infographic right now!

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual
communication in science.