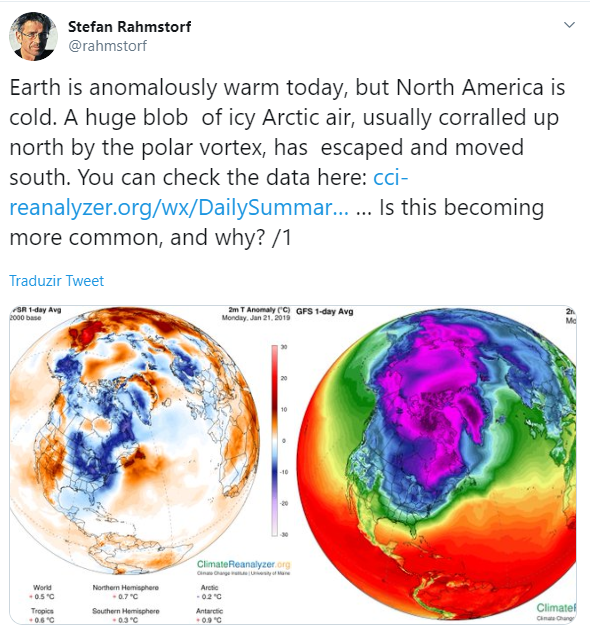
Yes. The global warming is real. At least according science. This is the short answer. But it is normal to be confused about the name global warming. Specially when winter is coming, you get cold and expect snowing for the weekend. So let’s see the newest scientific data to understand.
01. Climate X Weather
It isn’t the same thing. While weather is a temporary scale, climate is a long-term average. So even we keep experiencing cold days, this doesn’t nullify the arise of the global temperature. In fact, you can expect harsher winters in a warming world.
“Climate is defined as the average weather patterns in a region over a long period of time. It’s the difference between Europe’s temperate and Mediterranean zones versus the harsh cold conditions of the Arctic tundra. Each of these climate regions experiences day-to-day fluctuations in temperature, precipitation, air pressure, and so on—daily variations known as weather” (Source: National Geographic).
02. Extreme temperatures
The ‘Global warming’ term was coined a few decades ago. During that time, the main concern was about the greehouse gases heating the planet, increasing the average temperature. However the increase of carbon dioxide and methane gases in the atmosphere is causing more than temperature increase. As the Artic gets warmer, the winters in North America get colder.
Earth will experience more extreme, disastrous weather as the effects of climate change play out, not just heating.
Potsdam University physicist Stefan Rahmstorf explained on Twitter the relationship between cold days and global warming:

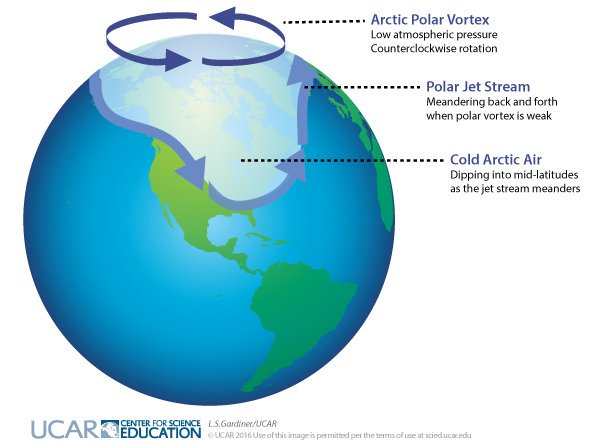
In fact, due to global warming, the North America should experience harsher winters. Two papers, one published on Nature communications and the other on Nature Geoscience found a link between warmer Arctic temperatures and colder North American winters.
The papers show that the occurrence of severe winter weather in the United States is significantly related to anomalies in pan-Arctic geopotential heights and temperatures. This relationship is strongest in the eastern US.
Warm Arctic Means Colder, Snowier Winters in Northeastern U.S.
“Basically, this confirms the story I’ve been telling for a couple of years now,” said study co-author Jennifer Francis, research professor of marine and coastal sciences in Rutgers’ School of Environmental and Biological Sciences. “Warm temperatures in the Arctic cause the jet stream to take these wild swings, and when it swings farther south, that causes cold air to reach farther south. These swings tend to hang around for awhile, so the weather we have in the eastern United States, whether it’s cold or warm, tends to stay with us longer.”
03. We should be getting colder
Global warming is just a natural cycle and we have nothing to do with it. Right? NO. I already wrote about the differences between natural cycles on Earth and the human caused climate change.
Possible Natural causes for the increasing temperatures:
The sun: Over the last 35 years the sun has shown a cooling trend. However global temperatures continue to increase.
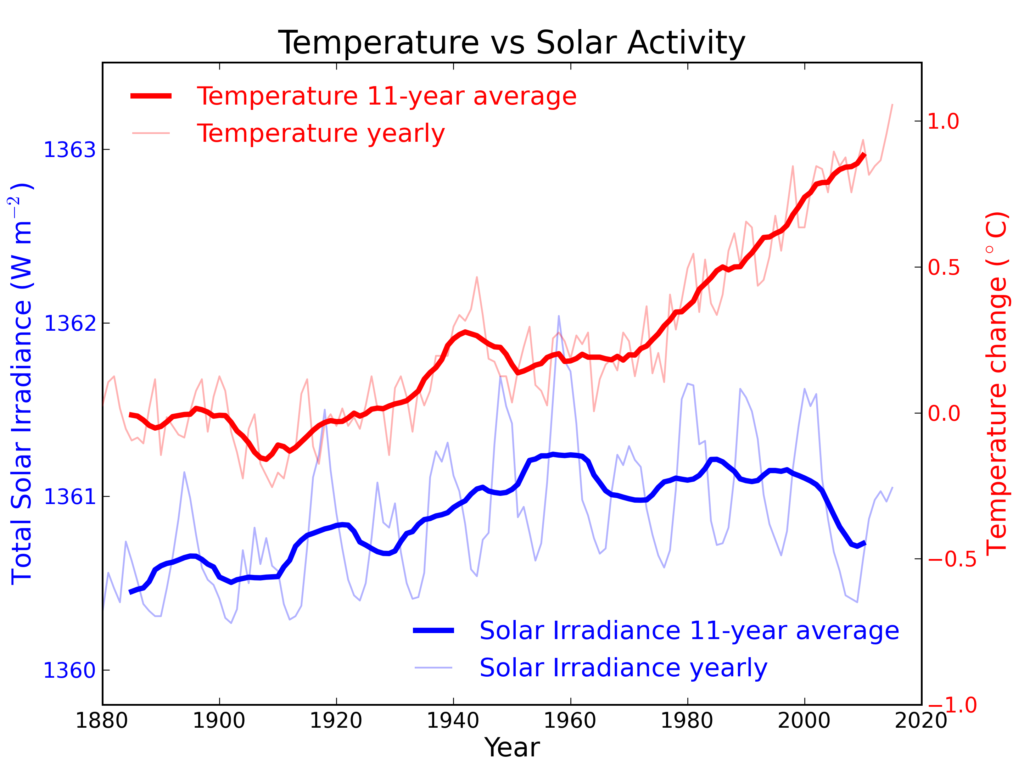
Pre Ice Age: Do you know that we are supposed going to another Ice Age, not a warm one?
Volcanism: Volcanos produce heat-trapping gases, so they can be the responsible for the temperature change, right? Actually, they produce less than 1% of the CO2 that humans produce. Also, big eruptions, when they happen, cool the Earth instead of warming it. The Nature paper entitled Last phase of the Little Ice Age forced by volcanic eruptions explain how the world started to move from a volcanically cooled era to a climate warmed by human emissions during the 18th Century.
Summarizing:
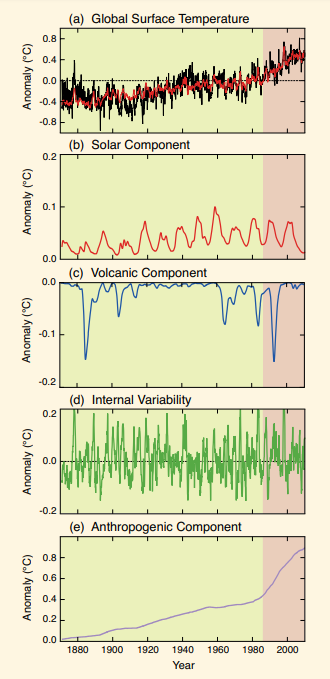
04. Temperature is increasing globally
The current scientific data points that before the Industrial Revolution the cold and warm periods didn’t happened globally.
The researchers studied the Little Ice Age, the coldest epoch of the last millennium. The results indicate that the coldest temperatures occurred during different centuries around the world. It took place during the 15th century in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, during the 17th century in northwestern Europe and southeastern North America. However, the remaining regions experienced the coldest temperatures only during the mid 19th century.
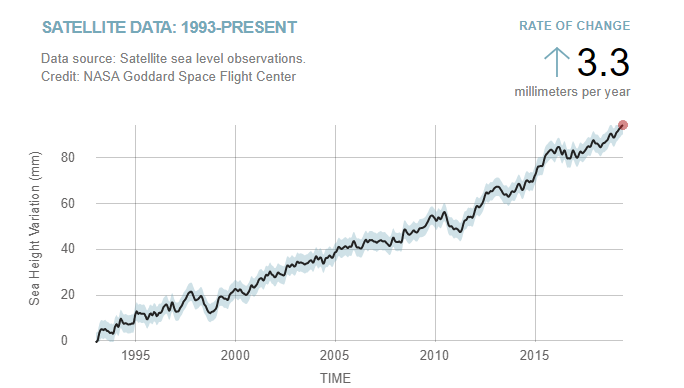
05. Sea level
First of all, we need to point the differences between Relative sea level change and absolute sea level:
- Relative sea level change is how the height of the ocean rises or falls relative to the land at a particular location.
- In contrast, absolute sea level change refers to the height of the ocean surface above the center of the earth, without regard to whether nearby land is rising or falling.
The seas rise unevenly — putting some communities even more at risk than others. Relative sea levels are different because local factors are at play, like land subsidence, wind and ocean circulations.
According to NASA, Sea level rise is caused primarily by two factors related to global warming: the added water from melting ice sheets and glaciers and the expansion of seawater as it warms.
To know more:
- Demystifying climate change through scientific data
- New scientific data stops climate change deniers

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual
communication in science.