Day after day, we depend on our muscles to hold our coffee, work on our laptops, and stroll to places. But, while it is uncommon, these same muscles can sometimes let us down.
All of those responsibilities are jeopardized due to autoimmunity and neurological illness. Continue reading to learn more about this extremely rare disorder.
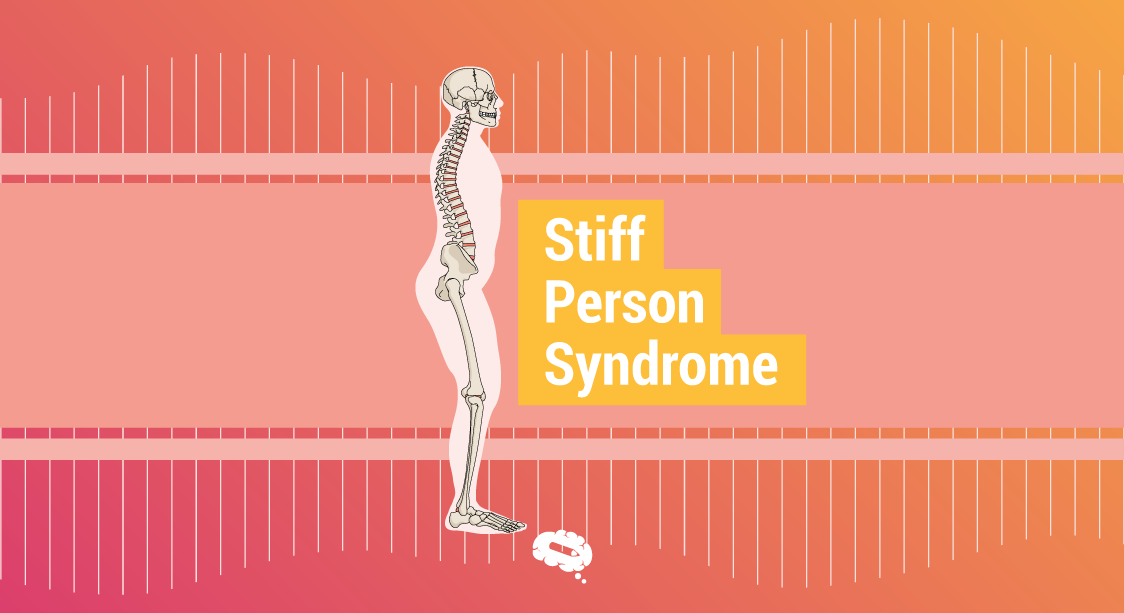
What is Stiff Person Syndrome?
Stiff-person syndrome, also known as Moersch-Woltman syndrome, is a rare neurological disorder with autoimmune characteristics, according to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Because of the condition, the body becomes stiff and more sensitive to sound, contact, and emotional distress. According to the institution, this increased sensitivity can result in muscular spasms in addition to hunched-over and tensed postures.
According to the Stiff Person Syndrome Research Foundation, muscular spasms can be so powerful that they can dislodge joints and perhaps even break bones.
Only one or two persons in a million suffer from stiff person syndrome, according to John Hopkins Medicine. Stiff person syndrome affects twice as many women as males. Symptoms can appear at any age, although they are most common between the ages of 30 and 60.
Symptoms and causes of Stiff Person Syndrome
Symptoms
The most significant aspect of this syndrome to emphasize is how unusual it is and how different individuals react; it is very common for some patients to stay stable for years, while others deteriorate rapidly.
The trunk and abdominal muscles are the first to stiffen and expand in most patients. Following that, it is usual to have the following symptoms:
- Pain;
- Muscle stiffness coming and going;
- Aching discomfort;
- Leg muscles stiffen with time, as other muscles throughout the body;
- Slumped-like posture;
- Difficulty to walk or move, due to stiffness;
- Long muscle spasms that can last for seconds, minutes or hours.
Causes
Although no reason for stiff person syndrome has been identified, researchers think it is an autoimmune disorder, which causes the immune system to destroy healthy cells. Individuals with this condition produce antibodies that assault a glutamic acid decarboxylase enzyme (GAD).
This enzyme is essential in the production of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that aids in muscle coordination. By targeting GAD, the body reduces the amount of GABA.
Yet, the function of GAD in the development and progression of stiff person syndrome is not completely known. In reality, some individuals with the condition do not have detectable GAD antibodies.
Another major factor that may contribute to the occurrence of this disease is the fact that a protein called amphiphysin is less common in people who have stiff person syndrome. This protein is essential for nerve cells to interact with one another and is located in nerve terminals.
How is Stiff Person Syndrome diagnosed and treated?
Diagnose
Stiff person syndrome symptoms are comparable to those of other illnesses such as tetanus, multiple sclerosis, and muscular dystrophies. It is frequently mistaken as other autoimmune conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease or an anxiety-phobia combo.
Several tests may be performed by the healthcare professional to rule out these disorders and check for evidence of stiff person syndrome, such as:
- Blood test: to test the presence of antibodies to GAC or amphiphysin, as well as other symptoms that might suggest or exclude other disorders.
- Lumbar puncture: An procedure that uses a needle to remove fluid from the spinal canal to test the presence of antibodies to GAC or amphiphysin, as well as other symptoms that might suggest or exclude other disorders.
- Electromyography (EMG): A machine detects ongoing motor activity in the muscles by measuring electrical activity in them.
Treatment
The treatments for stiff person syndrome will be decided based on the symptoms, with the objective of alleviating symptoms while increasing quality of life, such as mobility and comfort.
Treatment may include:
- Benzodiazepines, like diazepam and clonazepam or baclofen, to treat muscle stiffness;
- Anti-seizure drugs, anti-inflammatories and corticosteroids for pain;
- Physical therapy;
- Massages;
- Water therapy;
- Heat therapy;
- Acupuncture.
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), plasmapheresis, rituximab, and autologous stem cell transplant are other treatment options, however, they are less common.
Turn your data into easy-to-understand, dynamic stories
It is critical to ensure that your audience completely understands what you are saying when delivering important details in your work. Did you know that color visualizations improve people’s propensity to read a piece of text by 80%? (Source: Saurage Research) Make use of the Mind The Graph tool and select a template that best describes your work!

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual
communication in science.