Diabetes is a condition where you have a high blood sugar level and your system fails to have healthy sugar metabolism. It affects millions of people worldwide every year and has complications if not managed well. Read the article for understanding diabetes, its types, symptoms, and management.

What is Diabetes and Why is it Caused?
Diabetes occurs when glucose or blood sugar gets too high than normal level. It is a result of an inactive lifestyle, obesity, or poor diet.
Let’s understand the physiology of our body for understanding diabetes and how it is caused.
Carbohydrates are the major source of energy and our food comprises them adequately.
In the process of digestion of food, carbohydrates break down into glucose and are carried through the bloodstream to various organs of the body. Insulin is produced in the pancreas and is necessary for glucose intake in the cells and it prevents excess sugar in the blood.
But when a person is suffering from diabetes, the production of insulin is affected (either reduced or restricted) and the target cells reject taking up the glucose. This results in the accumulation of excess glucose in the bloodstream and a rise in the blood sugar level.
Recommended blood glucose levels in diabetes patients:
- Before meal – 80-130 mg/dl
- After a meal (between an interval of 2 hours) – 180 mg/dl
Symptoms of Diabetes
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Excess sweating
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Unexpected weight-loss
- Numbness or tingling feeling
- Increased hunger
- Delay in healing cuts and wounds
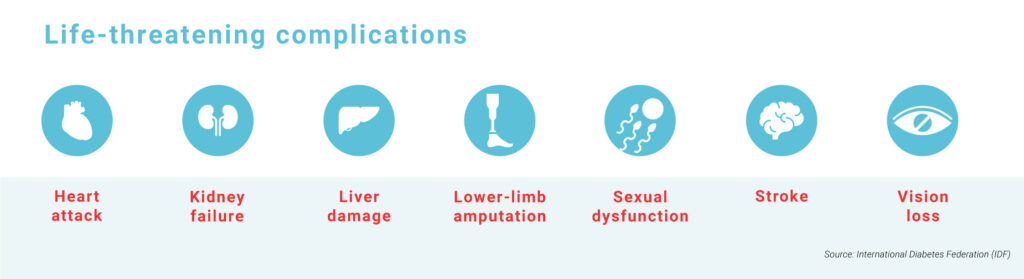
Complications of Diabetes
When a person has a high blood sugar level and it isn’t controlled timely, it might lead to severe health issues. The following might be the complications of diabetes:
- Kidney failure
- Heart problems
- Damage blood vessels
- Distort brain and nerve functioning
- Affect vision and damages the eyes
- Lead to Depression
- Increase foot problems
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
Popularly known as auto-immune disease or juvenile diabetes, this condition is dependent on insulin and is an immune system disorder. According to the CDC, 5-10% of total diabetic patients have Type 1 diabetes.
In type 1 diabetes, the person’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells, thereby hindering the production of insulin, and therefore, you’ll need to take insulin dosage regularly to live. It is a hereditary disorder that generally occurs at an early age and is most probably observed in children and young adults.
Type 2 Diabetes
This type is popularly known as insulin-resistant diabetes as the insulin is produced in the patient’s body but either it isn’t sufficient or doesn’t work correctly. While Type 2 diabetes isn’t as severe as Type 1, in this condition, your body doesn’t make sufficient insulin or fails to use the insulin properly, and this becomes the reason for a spike in blood sugar levels.
According to the CDC, 90-95% of total diabetic patients have Type 2 diabetes. It generally develops with aging but nowadays, it is also observed in children, teens, and young adults.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition where insulin isn’t used effectively in a woman when she’s pregnant. It might disappear after childbirth but raises her child’s risk of getting obese. It also increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes in the mother and baby in the later stages.
Prediabetics
Prediabetics is a condition when the blood sugar levels are on the borderline, i.e., higher than the normal level but lower than the type 2 diabetic conditions. With precautions, prediabetes can be avoided completely.
Management of Diabetes
While there is no proven evidence to cure diabetes, following these changes can help you live with it without incurring severe health risks.
- Make Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise of at least 30 minutes a day, five days a week can help you with weight loss and reduce the risk of obesity, thereby, helping you live healthy even with diabetes.
- Have a Healthy Diet: Limiting your carb intake and incorporating a balanced diet with whole grains, lentils, beans, fresh vegetables, fruits, dairy products, fish, lean meat, etc., can help you control your blood sugar levels.
- Take Medication: Following prescribed medication and taking it timely can help you manage diabetes.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking narrows your blood vessels and distorts your blood flow in the heart and feet, making it difficult for you to manage diabetes. So it’s advisable to quit smoking and start a healthy lifestyle.
- Manage Blood pressure and Cholesterol: High blood pressure and cholesterol can invite complications, so it’s quintessential to control your blood pressure and bad cholesterol. The recommended range of blood pressure for people with diabetes is 140/90 mm Hg.
- Take Regular Health Check-ups: Meeting your doctor regularly and keeping a check on your blood glucose levels and other health conditions helps you prevent any complications and health risks.
Explore the power of scientific illustrations
Nothing can beat a flawless visual piece when it comes to scientific research and explaining a complex message. Mind the Graph is an infographic platform that breaks down your concept into easy-to-understand images. Sign Up now to make your research process simple.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual
communication in science.