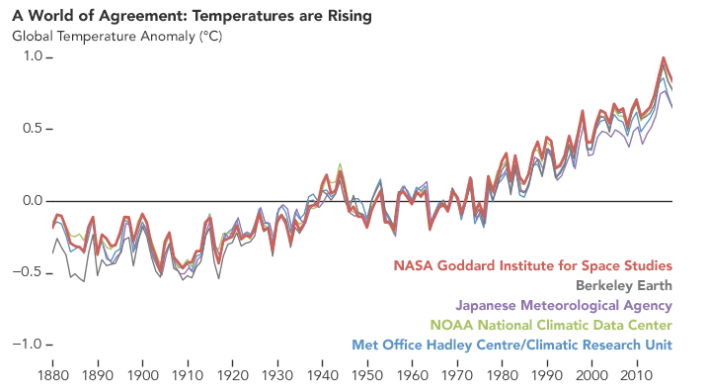
When you are learning about climate change and global warming, there must’ve been a point where you might have confused those two. But is climate change the same as global warming? That’s what we are going to dissect about in this article. By the end of this content, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to identify climate change and global warming distinctly.
Is Climate Change The Same As Global Warming? Understanding The Difference
Global warming specifically describes the increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels which releases greenhouse gasses like carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This warming effect is a component of the broader concept of climate change.
On the other hand, climate change includes global warming and a wider range of changes happening to our planet. These changes involve shifts in weather patterns, such as alterations in precipitation, more frequent and severe weather events like hurricanes and droughts, and changes in sea levels. Climate change refers to long-term changes in temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and other aspects of the Earth’s climate system.
So, to put it simply, global warming refers specifically to the Earth’s rising surface temperature, while climate change includes global warming and other long-term changes to the planet’s climate. Understanding this distinction helps us recognize the various impacts of human activities on our environment and underscores the complexity of the issues we face.
Detailed Look At The Two Concepts
Climate Change
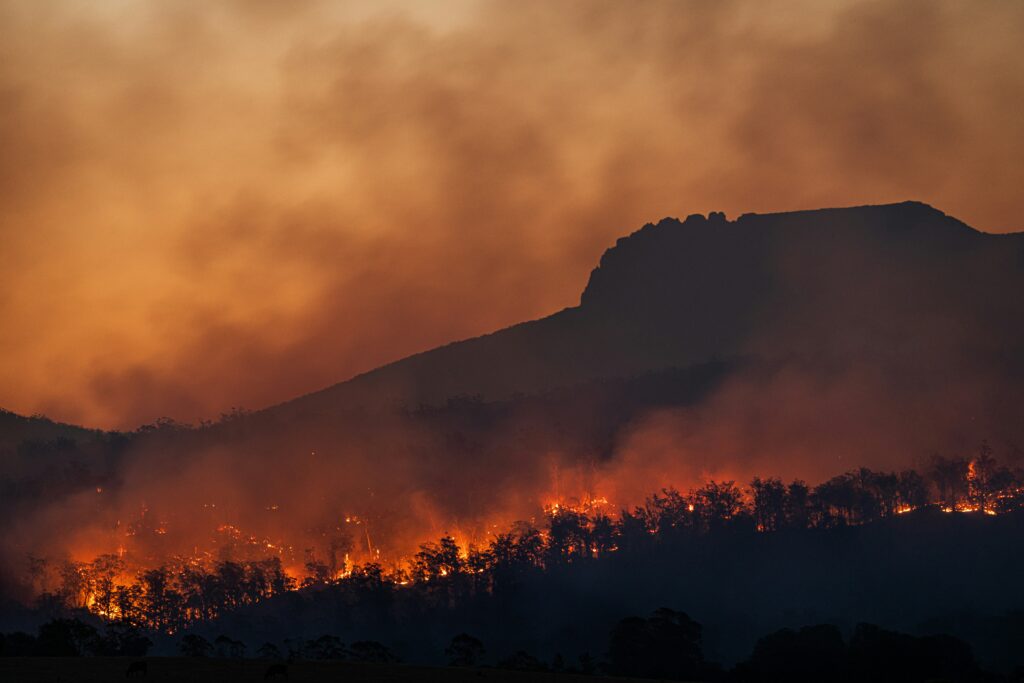

Climate change refers to significant, long-term changes in the Earth’s climate. This concept includes variations in temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and other climate indicators over extended periods. These changes can result from natural processes, such as volcanic eruptions and variations in solar radiation, as well as human activities.
Broad Effects
The effects of climate change are widespread and varied. They include:
Rising Sea Levels: As global temperatures increase, polar ice caps and glaciers melt, adding more water to the oceans. Additionally, warmer water expands, further contributing to sea level rise.
Extreme Weather Events: Increased temperatures can lead to more frequent and severe weather events, such as hurricanes, droughts, and heavy rainfall. These events can have devastating impacts on communities, economies, and ecosystems.
Changes in Ecosystems and Wildlife: As the climate changes, habitats and ecosystems can be altered, forcing wildlife to migrate, adapt, or face extinction. Changes in temperature and precipitation can affect plant growth, water availability, and the distribution of species.
Impacts on Human Health: Climate change can also impact human health by affecting air quality, increasing the spread of diseases, and causing heat-related illnesses.
Global Warming
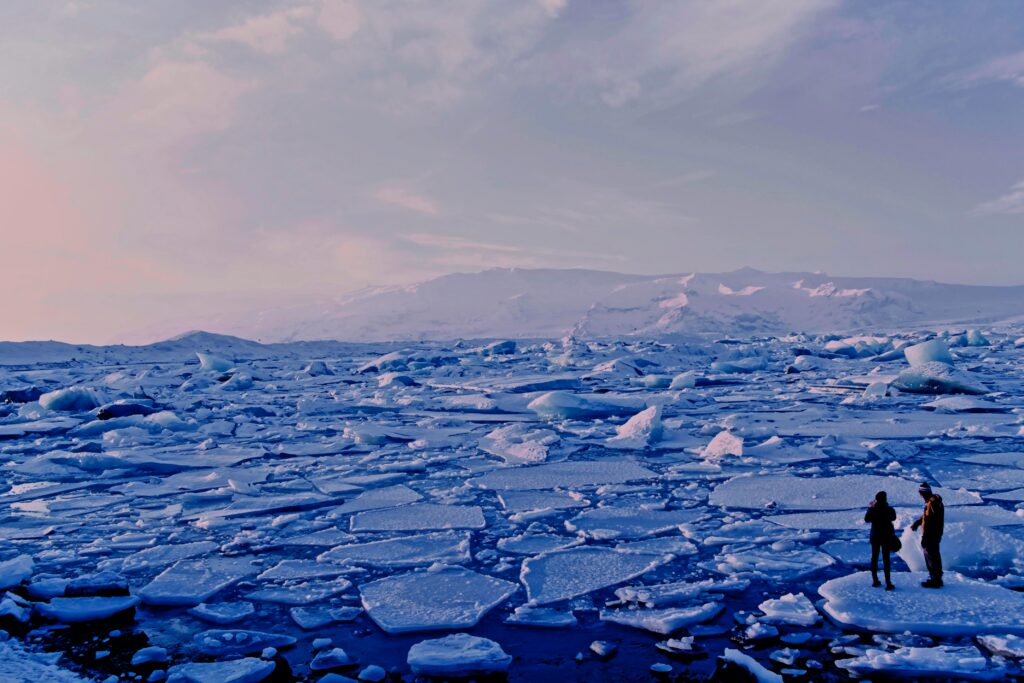

Global warming is a particular aspect of climate change that refers to the increase in Earth’s average surface temperature. This phenomenon is primarily driven by human activities, especially the burning of fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere.
Temperature Focus
The main focus of global warming is the rise in temperatures on the Earth’s surface. This temperature increase contributes to melting ice caps and glaciers, rising sea levels, and warming oceans. While global warming is a key driver of climate change, it specifically addresses the issue of temperature increases rather than the broader range of climate changes.
Impacts of Temperature Rise
Melting Ice and Glaciers: The rising temperatures contribute to the melting of ice sheets and glaciers, leading to rising sea levels.
Heatwaves: Increased global temperatures result in more frequent and intense heat waves, which can have severe impacts on agriculture, water supply, and human health.
Ocean Warming: The oceans absorb much of the excess heat from global warming, leading to thermal expansion and contributing to sea level rise. Warmer ocean temperatures also affect marine life, including coral reefs, which are highly sensitive to temperature changes.
While global warming focuses on the rise in Earth’s average surface temperature due to human activities, climate change encompasses this warming along with a broader range of changes in climate patterns, extreme weather events, and impacts on ecosystems and human societies.
Causes Of The Two Phenomenon
Climate Change Causes
Natural Processes
Climate change can be driven by natural processes such as volcanic eruptions, which release particles and gasses into the atmosphere, affecting global temperatures. Changes in the sun’s intensity, variations in Earth’s orbit, and natural carbon cycle fluctuations also contribute to long-term climate shifts.
Human Activities
Human activities significantly contribute to climate change. Deforestation, industrial processes, and agriculture release large amounts of greenhouse gasses, such as carbon dioxide and methane, into the atmosphere. These activities enhance the natural greenhouse effect, leading to changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and other climate-related factors.
Also Read: Demystifying Climate Change Through Scientific Data
Global Warming Causes
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The primary cause of global warming is the increase in greenhouse gas emissions. These gasses, including carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, trap heat in the atmosphere. The accumulation of these gasses enhances the natural greenhouse effect, causing the Earth’s average surface temperature to rise.
Fossil Fuel Burning
Burning fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is the main source of greenhouse gas emissions. This process releases significant amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. The widespread use of fossil fuels for energy production, transportation, and industry has greatly accelerated the rate of global warming.
While natural processes play a role in climate change, human activities have become the dominant force, particularly through the emission of greenhouse gasses from burning fossil fuels, deforestation, industrial processes, and agriculture.
Global warming specifically focuses on the increase in Earth’s average temperature due to these emissions, with fossil fuel burning being the most significant contributor. Understanding these causes is essential for developing strategies to mitigate climate change and reduce global warming.
Impacts Of Global Warming And Climate Change
On The Environment
Ecosystem Alterations
Climate change affects ecosystems by altering habitats and the distribution of plant and animal species. Warmer temperatures can shift climate zones, forcing species to migrate to new areas. This can disrupt existing ecosystems, leading to changes in biodiversity and the balance of natural communities.
Sea-level Rise
One significant impact of climate change is the rise in sea levels. Melting ice caps and glaciers, along with the thermal expansion of seawater as it warms, contribute to higher sea levels. This rise can lead to coastal erosion, increased flooding, and the loss of habitat for plants, animals, and even humans in low-lying areas.
On Society
Agricultural Changes
Climate change can significantly impact agriculture. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect crop yields, growing seasons, and the suitability of land for different types of farming. This can lead to food shortages, increased prices, and challenges for farmers trying to adapt to new conditions.
Health Risks
The effects of climate change also pose health risks to humans. Increased temperatures can lead to heatwaves, which can cause heat stroke and other heat-related illnesses. Changes in climate can also influence the spread of diseases, as warmer conditions may expand the range of vectors like mosquitoes. Additionally, extreme weather events and degraded air quality can have direct and indirect health impacts on communities.
The impacts of climate change on the environment and society are profound and far-reaching. Ecosystem alterations and sea-level rise pose significant threats to natural habitats and coastal areas, while agricultural changes and health risks challenge food security and public health.
Also Read: The Sustainability Science: Exploring Climate-Smart Agriculture
Mitigation And Adaptation Techniques
By Reducing Emissions
Renewable Energy
One effective way to mitigate climate change is by transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower. These sources produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gasses, significantly reducing our carbon footprint. Increasing the use of renewable energy can help lower global greenhouse gas emissions and slow the pace of global warming.
Energy Efficiency
Improving energy efficiency in homes, buildings, and industries is another crucial strategy for reducing emissions. This involves using technologies and practices that consume less energy to perform the same tasks, such as better insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and LED lighting. By reducing energy consumption, we can decrease the amount of fossil fuels burned and lower overall greenhouse gas emissions.
Also Read: Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Effect – A Scientific Infographic
Adapting To Changes
Infrastructure Adjustments
Adapting to climate change requires modifying our infrastructure to withstand its impacts. This includes building flood defenses, upgrading stormwater systems, and designing buildings that can cope with extreme weather events. Strengthening infrastructure helps communities become more resilient to climate-related disruptions and reduces the risk of damage.
Policy Changes
Governments play a vital role in adapting to climate change through policy changes. This involves creating and enforcing regulations that promote sustainable practices, such as emissions reduction targets, renewable energy incentives, and land-use planning.
Policies that support research, innovation, and community engagement are also essential for developing effective adaptation strategies and ensuring long-term sustainability.
Also Read: Climate Compensation: How Does Carbon Offsetting Work?
Public Perception Of Global Warming And Climate Change
Influence Of Media
The way media outlets use terminology significantly influences public perception of climate change and global warming:
- Global Warming vs. Climate Change: Media often use “global warming” and “climate change” interchangeably, but they convey different messages. “Global warming” emphasizes rising temperatures, which can lead some to think only about heat. “Climate change” encompasses a broader range of changes, including extreme weather events and ecological shifts. The choice of terms can shape how the public understands and prioritizes these issues.
- Framing and Messaging: How media frame climate-related stories affects public understanding and concern. For instance, framing climate change as a distant, future problem can lead to complacency, while highlighting immediate and local impacts can spur action. Additionally, sensationalist headlines might grab attention but can also lead to misinformation or climate fatigue.
Impact On Awareness
Media play a crucial role in raising awareness and shaping public opinion on climate issues:
- Highlighting Impacts: Media reports on climate-related disasters, such as hurricanes, wildfires, and droughts, make the impacts of climate change more tangible to the public. Visual storytelling, including documentaries and news footage, can effectively convey the severity of these events.
- Influence of Social Media: Social media platforms amplify messages and enable grassroots movements to raise awareness and mobilize action. Hashtags, viral videos, and influential voices can spread information quickly, although they can also perpetuate misinformation if not carefully managed.
Education And Awareness Among People
Resources For Understanding
Access to educational resources is essential for fostering a comprehensive understanding of climate change and global warming. Books, documentaries, online courses, and reputable websites provide valuable information that helps individuals grasp the science behind these phenomena and their implications. These resources empower people to make informed decisions and take action.
Role Of Schools And Communities
Integrating climate education into school curricula at all levels ensures that students understand the science and implications of climate change. This includes teaching about greenhouse gasses, renewable energy, conservation practices, and the importance of sustainability. Encouraging critical thinking and problem-solving skills empowers students to become informed and active citizens.
Community programs, workshops, and local initiatives also contribute to raising awareness and promoting sustainable practices. Engaging communities in climate education fosters a collective effort to address and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Media influence and educational efforts are critical in shaping public perception and understanding of climate change. Accurate and responsible media coverage, coupled with comprehensive educational resources and community initiatives, can enhance awareness and motivate collective action.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between climate change and global warming is essential for informed discussions and effective action.
Global warming refers specifically to the rise in Earth’s average surface temperature due to elevated greenhouse gas levels, primarily from human activities. In contrast, climate change encompasses this warming along with broader changes in climate patterns, such as shifts in precipitation, extreme weather events, and ecosystem alterations.
Accurate terminology is important for clarity, effective communication, policy-making, and shaping public perception. Using precise language helps in comprehending the full scope of environmental challenges, fostering better-informed citizens, and promoting targeted and effective strategies to mitigate and adapt to these changes.
Your Creations, Ready Within Minutes!
Looking for scientific illustrations that can be found in a jiffy? Mind the Graph is the hotspot for all your creations that will be ready within minutes. Sign up now to explore the library of scientific visuals that cater to your needs.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual
communication in science.