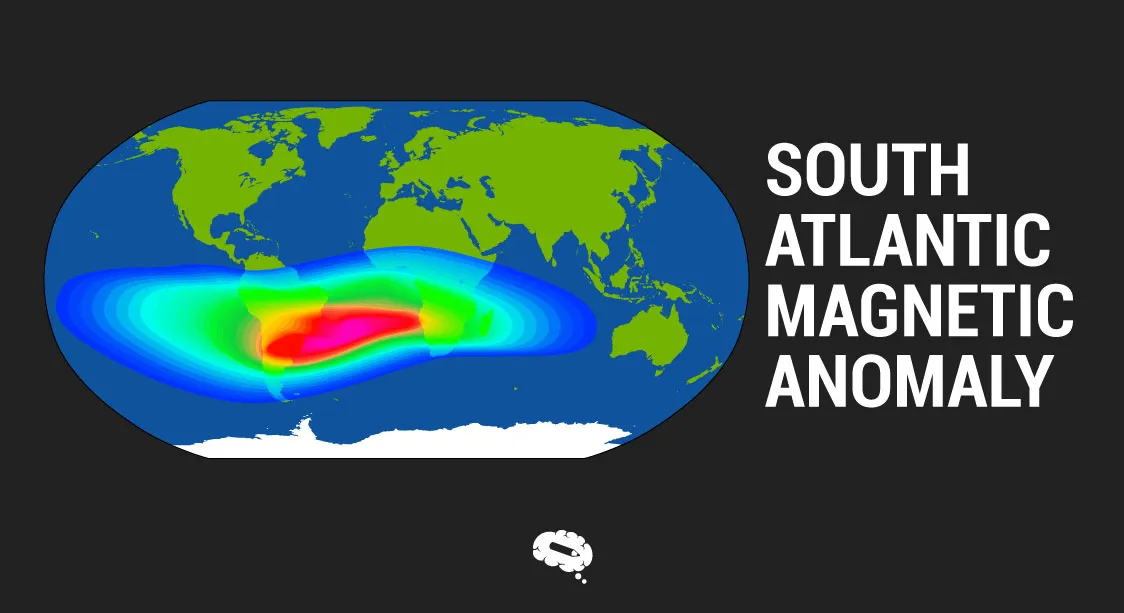
Den Sør-Atlanterhavets magnetiske anomali (SAMA) is one of the most intriguing and significant features in the study of Earth’s geomagnetic field. Located over the South Atlantic Ocean, this anomaly is characterized by an unusually weak magnetic field compared to the surrounding areas. It extends roughly from the southern tip of South America to the mid-Atlantic Ridge, encompassing parts of Brazil and Angola. The anomaly is not just a curious geological feature but a focal point for understanding the complexities and dynamics of Earth’s magnetic field.
As this article delves deeper into the South Atlantic Magnetic Anomaly, you’ll uncover more about its origins, current behavior, and potential future developments. This exploration not only enhances our comprehension of Earth’s magnetic environment but also explains the potential challenges arising from this unique geomagnetic feature.
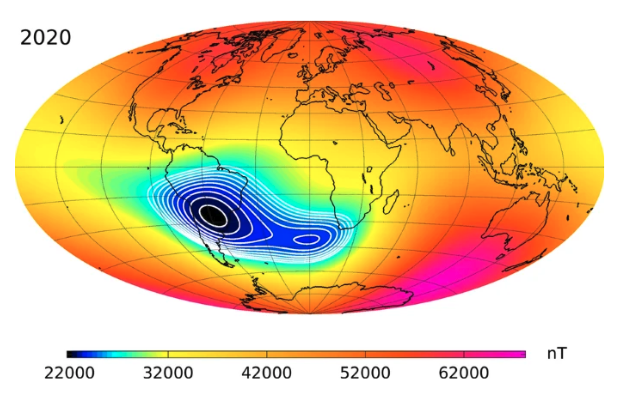
Hva er den søratlantiske magnetiske anomalien?
The South Atlantic Magnetic Anomaly (SAMA) is a region of Earth’s magnetic field characterized by an unusually low intensity of the magnetic flux density compared to other areas on the planet. This anomaly is situated over the South Atlantic Ocean and extends over parts of South America and Africa. The magnetic field strength in this region is significantly weaker than the global average, making it a focal point for scientific research and technological consideration.
The South Atlantic Magnetic Anomaly is part of a broader phenomenon known as geomagnetic secular variation, which involves changes in the Earth’s magnetic field over time. Its distinctive feature is the notable decrease in magnetic field strength, which contrasts sharply with the more robust magnetic field observed in other regions.
Betydning
Den søratlantiske magnetiske anomalien er av stor interesse for forskere og ingeniører av flere grunner:
- Vitenskapelig forskning: Understanding the SAMA provides insights into the dynamics of Earth’s geomagnetic field and the processes occurring in the planet’s outer core. Studying the anomaly helps researchers model the behavior of the geodynamo—the mechanism that generates Earth’s magnetic field—and track its variations over time. This knowledge is crucial for understanding the long-term changes in Earth’s magnetic field and its impact on the planet’s environment.
- Påvirkning på jorden: Det svekkede magnetfeltet i SAMA-regionen fører til økt eksponering for kosmisk stråling og solstråling. Dette kan ha ulike effekter på både naturlige systemer og menneskeskapt infrastruktur. For eksempel kan økte strålingsnivåer påvirke atmosfæriske prosesser og potensielt påvirke klimamønstrene.
- Teknologiske implikasjoner: SAMA byr på spesielle utfordringer for teknologi og romferder. Satellitter som passerer gjennom dette området, utsettes for høyere strålingsnivåer, noe som kan føre til elektroniske feil og skader. Dette kan påvirke satellittenes ytelse, kommunikasjon og dataintegritet. I tillegg kan anomalien forstyrre globale navigasjonssystemer, ettersom variasjoner i magnetfeltet kan påvirke kompassavlesninger og navigasjonsnøyaktighet.
In summary, the South Atlantic Magnetic Anomaly is a significant feature of Earth’s magnetic field with far-reaching implications for both scientific understanding and technological operations. Its study helps advance our knowledge of geomagnetic processes and informs strategies to mitigate the effects on technology and infrastructure.
Årsaker til den søratlantiske magnetiske anomalien
To understand the South Atlantic Magnetic Anomaly (SAMA), it is essential to explore the factors contributing to its formation. This anomaly is not an isolated phenomenon but rather a manifestation of broader processes affecting Earth’s magnetic field. Investigating the underlying causes provides insight into how such anomalies arise and what they reveal about Earth’s dynamic systems.
The origins of the South Atlantic Magnetic Anomaly are rooted in the fundamental workings of Earth’s magnetic field and the geological processes influencing it. By examining the basics of geomagnetic field generation and the specific geological factors involved, a clearer picture of this intriguing magnetic feature emerges.
The following sections will delve into the fundamental principles of Earth’s magnetic field and how the SAMA fits into this larger context, followed by an exploration of the geological factors and current theories explaining its existence and behavior.
Earth’s Magnetic Field
Earth’s magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is generated by the movement of molten iron and other materials in the planet’s outer core. This movement creates electric currents, which in turn generate magnetic fields. The combined effect of these fields produces a complex, dynamic magnetic environment that extends from the core to the space surrounding Earth.
The geomagnetic field is generally dipolar, meaning it has two main poles—north and south—that are roughly aligned with the planet’s rotational axis. However, this field is not perfectly uniform; it exhibits variations due to the irregularities in the flow of molten iron in the outer core, as well as influences from the Earth’s crust and mantle.
The South Atlantic Magnetic Anomaly represents a significant deviation from the normal geomagnetic field. In this region, the magnetic field strength is substantially lower than the global average. This anomaly does not fit neatly into the dipolar model of the geomagnetic field and instead represents a localized weakening of the magnetic flux density. Understanding how the SAMA fits into the broader geomagnetic system requires examining the interplay between the Earth’s core processes and surface characteristics.
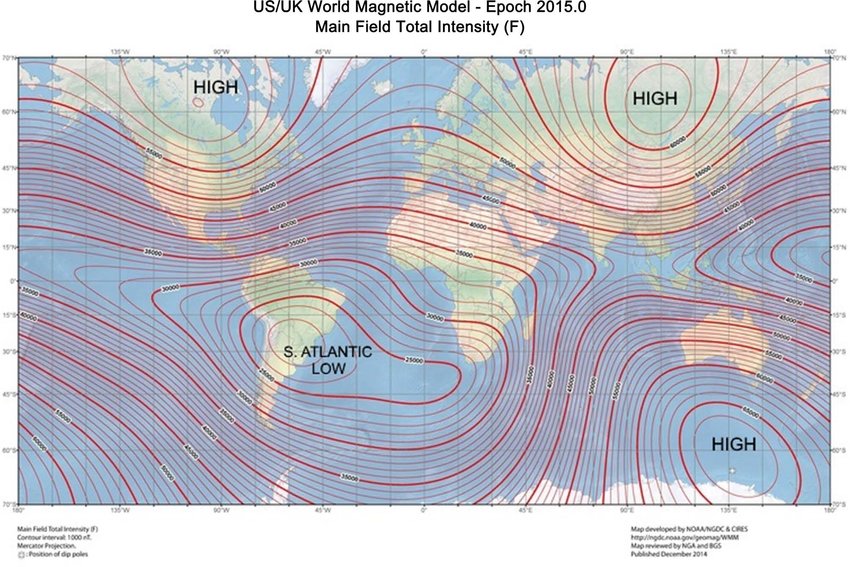
Geologiske faktorer
Den søratlantiske magnetiske anomalien antas å være påvirket av flere geologiske og geofysiske faktorer:
- Geodynamodynamikk: The primary driver of Earth’s magnetic field is the geodynamo, which involves the movement of molten iron in the outer core. Variations in the flow and temperature of this molten material can lead to fluctuations in magnetic field strength. The SAMA is thought to be associated with a region where the geodynamo’s processes are less efficient, resulting in weaker magnetic field strength.
- Mantelkonveksjon: Another contributing factor could be the patterns of mantle convection. The flow of material in the Earth’s mantle affects the distribution of heat and the dynamics of the outer core. Variations in mantle convection can influence the geodynamo and, consequently, the strength and distribution of the geomagnetic field.
- Innflytelse fra jordskorpen: The Earth’s crust and upper mantle can also play a role in shaping the magnetic field. Localized variations in magnetic properties due to the presence of different types of rocks or mineral deposits can contribute to the formation of anomalies like the SAMA. These crustal effects can modulate the overall magnetic field in specific regions.
- Aktuelle teorier og forskning: Nyere forskning har fokusert på å forstå samspillet mellom disse ulike faktorene for bedre å kunne forklare SAMA. Studier ved hjelp av satellittdata og datasimuleringer har gitt innsikt i geodynamoens virkemåte og dens innvirkning på magnetfeltet. Forskere har for eksempel undersøkt hvordan svekkelsen av magnetfeltet i SAMA-regionen kan henge sammen med mer generelle trender i geomagnetisk feltstyrke og polaritetsreversering.
Effekter av den søratlantiske magnetiske anomalien
The South Atlantic Magnetic Anomaly (SAMA) has notable effects on various technological systems, primarily due to its influence on Earth’s magnetic field. Understanding these effects is crucial for mitigating potential disruptions and enhancing the resilience of technological and navigational systems that operate in or near the anomaly’s region.
This section examines the impact of the SAMA on two critical areas: satellites and navigation systems. The anomaly’s weakened magnetic field can lead to significant challenges for space missions and satellite operations, while its effects on navigation systems can disrupt the accuracy of both aerial and maritime navigation. By exploring these impacts, one can appreciate the broader implications of the SAMA on modern technology and infrastructure.
Påvirkning på satellitter
Den søratlantiske magnetiske anomalien (SAMA) påvirker satellitter og romfartsmisjoner i betydelig grad på grunn av de økte strålingsnivåene i denne regionen. Det svekkede magnetfeltet gjør at mer kosmisk stråling og solstråling trenger inn, noe som kan ha flere skadelige effekter på satellittenes drift og ytelse.
Hvordan anomalien påvirker satellitter og romferder
Satellites traversing the SAMA encounter elevated radiation levels, which can lead to disruptions in their electronic systems. This increased radiation exposure can result in data corruption, malfunctions in electronic components, and potential damage to sensitive instruments. The anomaly’s effects can compromise satellite functionality, including its communication systems and onboard sensors, impacting data integrity and mission success.
Spesifikke eksempler på satellittfeil
Flere satellitter har opplevd problemer knyttet til SAMA. For eksempel:
- Hubble-romteleskopet: Hubble-romteleskopet har opplevd midlertidige funksjonsfeil og dataavvik når det har passert gjennom SAMA, noe som tilskrives strålingsinduserte forstyrrelser.
- GOES-13: Denne værsatellitten opplevde problemer med sensorene og kommunikasjonssystemene under passasjen gjennom SAMA, noe som påvirket værovervåkingskapasiteten.
These examples illustrate how the SAMA’s radiation environment can impact satellite operations, underscoring the need for careful planning and shielding to mitigate these effects.
Innvirkning på navigasjonen
Den søratlantiske magnetiske anomalien forstyrrer også navigasjonssystemene, noe som påvirker både luft- og sjønavigasjon. Det svekkede magnetfeltet i denne regionen kan føre til unøyaktigheter i magnetisk baserte navigasjonssystemer, som er avhengige av stabile magnetfeltavlesninger.
Hvordan det forstyrrer navigasjonssystemene
Magnetic compasses and other navigation systems that rely on Earth’s magnetic field can experience deviations when operating within the SAMA. This can lead to incorrect readings, requiring compensatory adjustments to maintain accurate navigation. The anomaly’s impact is particularly pronounced for systems that depend on precise magnetic field measurements.
Effekter på fly og skip
For fly kan SAMA føre til avvik i navigasjonssystemene om bord, noe som kan påvirke flytraseer og sikkerhet. Piloter må kanskje ta høyde for økt magnetisk interferens, noe som kan komplisere navigasjonen og kreve ytterligere verifisering ved hjelp av alternative systemer.
I maritim navigasjon kan skip som bruker magnetkompass eller GPS-systemer, oppleve navigasjonsfeil eller redusert nøyaktighet når de opererer innenfor SAMA. Dette kan påvirke ruteplanleggingen og navigeringen, noe som gjør det nødvendig med ekstra kontroller og bruk av supplerende navigasjonshjelpemidler.
Den søratlantiske magnetiske anomalien skaper utfordringer for navigasjonssystemene, og påvirker både luft- og sjøtransport ved å introdusere potensielle unøyaktigheter og kreve justeringer for å sikre pålitelig og nøyaktig navigasjon.
Forskning og studier
The South Atlantic Magnetic Anomaly (SAMA) has garnered significant attention from the scientific community due to its impact on Earth’s magnetic field and technological systems. As researchers and institutions continue to investigate this anomaly, new insights are being gained into its causes and effects. Ongoing research and technological advancements are crucial for understanding and mitigating the challenges posed by the SAMA.
Denne delen gir en oversikt over den nåværende forskningsinnsatsen som fokuserer på SAMA, og fremhever viktige organisasjoner og institusjoner som er involvert i studiet av anomalien. Vi ser også nærmere på de teknologiske fremskrittene som er utviklet for å løse utfordringene knyttet til SAMA, og skisserer mulige fremtidige forskningsretninger.
Pågående forskning
En rekke organisasjoner og institusjoner er opptatt av å studere den søratlantiske magnetiske anomalien, fordi den har stor betydning for både vitenskapelig forståelse og praktisk anvendelse.
Organisasjoner og institusjoner som studerer anomalien
- NASA: The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) conducts extensive research on the SAMA through its space missions and satellite observations. NASA’s space missions provide valuable data on the anomaly’s impact on satellites and help refine models of Earth’s magnetic field.
- ESA: The European Space Agency (ESA) also plays a critical role in studying the SAMA. ESA’s space missions, such as the Swarm satellite mission, focus on mapping Earth’s magnetic field and investigating regional anomalies, including the SAMA.
- National Geographic Society: This organization supports research on geomagnetic phenomena and funds studies aimed at understanding the broader implications of the SAMA on Earth’s environment.
Aktuelle oppdrag og studier
- Satellittoppdraget Swarm: ESA’s Swarm mission, launched in 2013, is a key project in the study of Earth’s magnetic field. The mission aims to provide detailed data on the magnetic field and its anomalies, including the SAMA, by deploying a constellation of three satellites.
- NASA’s Magnetic Field Missions: NASA’s missions, such as the Magnetic Field Investigation (MFI), focus on understanding the dynamics of Earth’s magnetic field and its variations, including those observed in the South Atlantic region.
- Geofysiske forskningsstudier: Geofysikere og forskere fra ulike institusjoner forsker på de underliggende mekanismene bak SAMA og samspillet med geodynamoen og mantelkonveksjonen.
Teknologiske fremskritt
Teknologiske fremskritt bidrar til å løse utfordringene som følger av den søratlantiske magnetiske anomalien. Nyvinninger innen satellittdesign og navigasjonssystemer er avgjørende for å dempe effekten av anomalien og forbedre driftssikkerheten.
Ny teknologi utviklet for å håndtere anomalien
- Strålingsskjerming: Ny teknologi innen strålingsskjerming er utviklet for å beskytte satellitter mot økt strålingseksponering i SAMA-regionen. Avanserte materialer og skjermingsteknikker bidrar til å redusere risikoen for elektroniske feil og skader.
- Forbedrede navigasjonssystemer: Det utvikles forbedrede navigasjonssystemer som integrerer flere datakilder, blant annet GPS og treghetsmåleenheter, for å kompensere for magnetfeltforvrengningene som forårsakes av SAMA. Disse systemene gir mer nøyaktig og pålitelig navigasjonsinformasjon.
- Algoritmer for datakorrigering: Forskere utvikler avanserte algoritmer for datakorreksjon for å ta hensyn til avvik i magnetfeltet. Disse algoritmene bidrar til å filtrere bort forvrengninger i data som samles inn fra satellitter og navigasjonssystemer, noe som forbedrer den generelle nøyaktigheten.
Fremtidige forskningsretninger
- Avanserte geomagnetiske modeller: Future research aims to develop more precise models of Earth’s geomagnetic field that incorporate detailed data on anomalies like the SAMA. These models will improve predictions of field variations and their effects.
- Langsiktig overvåking: Fortsatt langsiktig overvåking av SAMA og endringene i den er avgjørende for å forstå hvordan den oppfører seg, og for å forutsi fremtidige konsekvenser. Pågående satellittoppdrag og bakkebaserte studier vil bidra til en mer omfattende forståelse av anomalien.
- Innovativ romfartøydesign: Fremtidige romfartøyer og satellitter vil bli konstruert med avansert teknologi for å tåle effekten av SAMA bedre. Forskning på nye materialer og tekniske løsninger vil forbedre holdbarheten og ytelsen til romfartøyer som opererer i denne regionen.
Potensielle utfordringer
The South Atlantic Magnetic Anomaly (SAMA) presents a range of challenges that impact both scientific research and practical applications. These challenges arise from the anomaly’s effects on technology, navigation, and our understanding of Earth’s magnetic field. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research and innovative solutions.
Teknologiske utfordringer
- Sårbarheter i satellitter: Satellitter som passerer gjennom SAMA, utsettes for høyere nivåer av stråling, noe som kan forårsake elektroniske feil, datakorrupsjon og til og med fysisk skade på følsomme komponenter. Den økte strålingen kan påvirke satellittens ytelse og føre til problemer med kommunikasjon, dataoverføring og generell pålitelighet.
- Strålingsinduserte feil: The anomaly’s radiation environment can induce failures in electronic systems onboard satellites and space missions. This includes the risk of electronic component degradation, increased error rates in data processing, and potential short-term or long-term operational disruptions.
- Økte driftskostnader: For å håndtere konsekvensene av SAMA kreves det ofte ekstra ressurser, for eksempel bedre skjerming av satellitter eller hyppigere vedlikehold og kalibrering. Disse tiltakene kan øke kostnadene for romferder og satellittoperasjoner.
Navigasjon og operasjonelle utfordringer
- Unøyaktige målinger av magnetfelt: SAMA medfører betydelige avvik i magnetfeltavlesningene, noe som kan påvirke systemer som er avhengige av magnetkompass eller magnetisk basert navigasjonsteknologi. Disse unøyaktighetene kan komplisere navigasjonsoppgavene, slik at piloter og skipsnavigatører må bruke tilleggssystemer eller utføre ekstra kontroller.
- Justeringer av flyrute: For fly kan magnetfeltforvrengningene som forårsakes av SAMA, føre til unøyaktigheter i navigasjonssystemene om bord, noe som kan gjøre det nødvendig å justere flyrutene og kreve ekstra inngripen fra piloten for å sikre nøyaktig navigasjon.
- Maritime navigasjonsspørsmål: Skip som navigerer gjennom SAMA kan oppleve forstyrrelser i magnetiske kompassavlesninger, noe som kan føre til potensielle avvik fra tiltenkt kurs. Dette kan komplisere navigasjonen til sjøs og gjøre det nødvendig å bruke alternative navigasjonshjelpemidler for å opprettholde nøyaktigheten.
Vitenskapelige og forskningsmessige utfordringer
- Kompleksiteten i geomagnetiske modeller: Understanding the SAMA requires complex geomagnetic models that account for variations in Earth’s magnetic field. Developing and refining these models is challenging due to the dynamic nature of the geodynamo and the variability in magnetic field strength.
- Langsiktig overvåking: Kontinuerlig og langsiktig overvåking av SAMA er nødvendig for å følge utviklingen og forstå hvordan den oppfører seg. Dette krever vedvarende finansiering og ressurser til satellittoppdrag, bakkebaserte observasjoner og dataanalyse.
- Tolkning av data: Det kan være utfordrende å analysere data som samles inn fra satellitter og andre kilder i SAMA-regionen på grunn av anomalier og støy. Forskere må utvikle sofistikerte algoritmer og teknikker for datakorreksjon for å kunne tolke og bruke disse dataene på en nøyaktig måte.
Den søratlantiske magnetiske anomalien byr på betydelige utfordringer på en rekke områder, fra teknologiske konsekvenser for satellitter og navigasjonssystemer til kompleksiteten i vitenskapelig forskning og datatolkning. For å løse disse utfordringene kreves det en mangefasettert tilnærming som involverer avansert teknologi, kontinuerlig overvåking og innovative forskningsstrategier.
Revolusjoner vitenskapelig kommunikasjon med Mind the Graph!
Mind the Graph revolusjonerer vitenskapelig kommunikasjon ved å tilby en avansert plattform for å skape visuell kommunikasjon med stor gjennomslagskraft. Forskere, undervisere og vitenskapsformidlere kan bruke dette verktøyet til å oversette komplekse data til tydelig og engasjerende grafikk. Mind the Graph er avgjørende for å gjøre vitenskapelige presentasjoner tydeligere og mer effektive, og bygger bro mellom komplisert forskning og tilgjengelig visuell kommunikasjon. Registrer deg gratis og dykk ned i galleriet vårt med en gang.

Abonner på nyhetsbrevet vårt
Eksklusivt innhold av høy kvalitet om effektiv visuell
kommunikasjon innen vitenskap.