The last days were tough, right? The wildfires in the Amazon rainforest become a trend topic. In the last few days we stay very concerned about the rainforest, sustainability and the life on Earth in general. After all the discussion and reading, the conclusion is that we need to take action, as humans and as scientists. I wrote several articles about the climate change and the Amazon rainforest biodiversity to raise awareness about the importance to keep the forest alive.
Du kan se disse artiklene nedenfor:
- Nye vitenskapelige data stopper klimafornekteres
- Det underjordiske nettverket som holder regnskogen i live
- Det biologiske mangfoldet i Amazonas' regnskog i bilder
But today I want to talk about the latest science news in an optimistic way. We work in science to improve human lifes, discover more about life and universe and to change for the better, right?
So let’s check what other scientists are discovering. Follow the latest science news is important to improve communication in science and also keep the optimism. So, I want to share with you the best of science news:
CRISPR bremser veksten av trippelnegativ brystkreft hos mus:
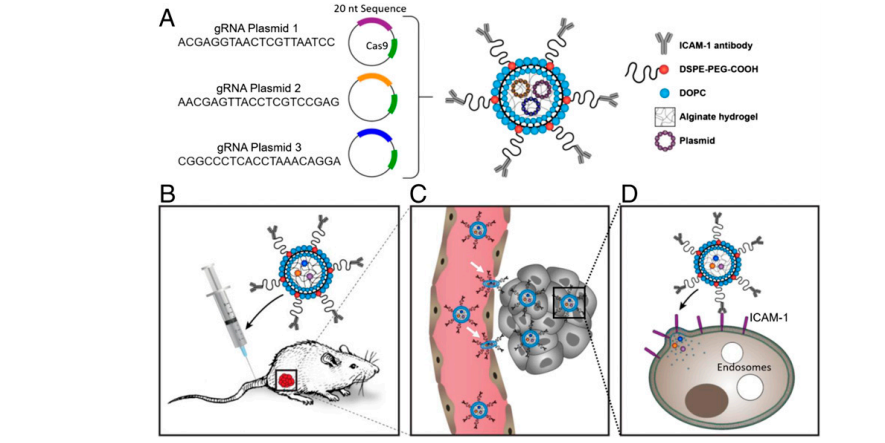
Et forskerteam ved Boston Children's Hospital har utviklet en innovativ måte å slå ut genet Lipocalin 2 på ved hjelp av redigeringssystemet CRISPR, og har vist at det har potensial til å behandle trippel-negative brystsvulster hos mus. Dette genet er knyttet til trippel-negativ brystkreft, en aggressiv form av sykdommen som det finnes få effektive, målrettede behandlinger for.
The graphical abstract made bu the authors shows the biomechanisms of in vivo CRISPR genome editing. You can see how the deformable nanostructure of the tumor targeted nanolipogel system (tNLG) significantly improves its capability to cross leaky tumor endothelial barriers. Arrows highlight the events of transendothelial delivery of tNLGs. For the last, you can see how CRISPR plasmids of tNLGs are directly released into the cytosol of targeted TNBC cells via ICAM1-mediated membrane fusion pathway.
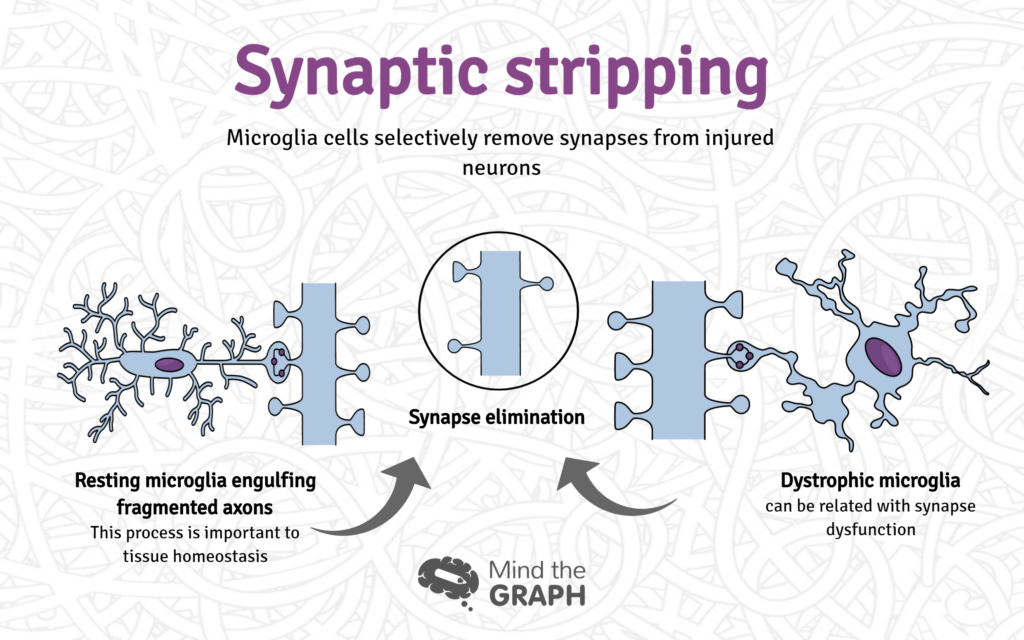
En ny studie viser at fysisk trening bedrer avvikene i omgjengelighet, repetitivitet og angst hos personer med nevroutviklingsforstyrrelser.
Physical exercise has attracted attention as a potential therapeutic strategy for abnormal behaviors in neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorders (ASDs). The authors examined the role of microglia in synaptic deficits in maternal immune activation (MIA) offspring. Microglia are the resident immune cells in the brain. The results revealed that exercise reversed the abnormal behaviors and synaptic surplus in adult MIA offspring. So exercise actives a portion of neurons, resulting in the engulfment of excess synapses by microglia, likely primed by synaptic competition.
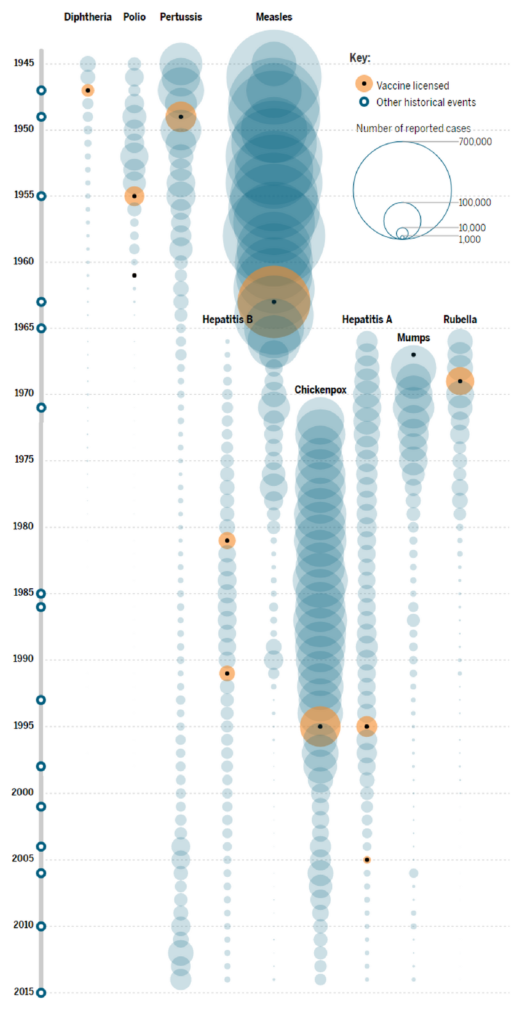
Polio er ikke lenger endemisk i Nigeria
Informasjonen kommer fra Verdens helseorganisasjon (WHO). Den 21. august kunngjorde de at Nigeria har markert tre år uten nye tilfeller av den lammende sykdommen. Dette er en veldig god nyhet! Antallet nye smittetilfeller har også falt globalt, fra rundt 350 000 i 1988 til 33 i 2018.
In the infographic below you can see how vaccination is related with the eradication of infectious diseases here:
Do you want to show your research in a visual and attractive way? Then try Mind the Graph:

Abonner på nyhetsbrevet vårt
Eksklusivt innhold av høy kvalitet om effektiv visuell
kommunikasjon innen vitenskap.